1. Introduction and Technical Information about Oxandrolone
Oxandrolone, a well-known anabolic androgenic steroid, stands out for its friendly side effect profile and effectiveness. Initially brought to the market in the 1960s under the name Anavar by G.D. Searle & Co., it was primarily developed for therapeutic applications. Despite its discontinuation in the late 1980s due to FDA pressure, Oxandrolone reemerged in the mid-1990s under a new brand, Oxandrin, and has since remained a prominent substance in both medical and athletic circles.
Oxandrolone Profile
- Chemical Structure: C19H30O3
- Typical Dosage: 5-100mg per day, depending on use and individual response
- Anabolic/Androgenic Ratio: 320-630:24
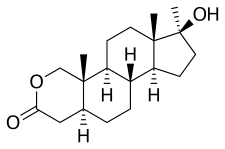
2. Oxandrolone Breakdown: Profiling Its Functional and Distinct Traits
As a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), Oxandrolone is characterized by the addition of an oxygen atom replacing carbon-2 in the A-ring, enhancing its anabolic potential. This structural alteration allows it to resist metabolic breakdown and categorizes it as a C17-alpha alkylated anabolic steroid, enabling oral administration without liver destruction.
3. Oxandrolone’s Diverse Impact: From Therapeutic to Performance Enhancement
Medically, Oxandrolone has been instrumental in aiding weight gain post-surgery or infection, treating osteoporosis, and countering excessive corticosteroid exposure. Its therapeutic efficacy extends to treating specific cases of hepatitis and hormone deficiencies in children. In the realm of performance enhancement, its high anabolic rating and low androgenicity make it a choice steroid for both men and women, particularly in preserving lean muscle during caloric deficits.
4. Understanding Oxandrolone: Side Effects and Administration Guidelines
Oxandrolone is celebrated for its low incidence of side effects, making it a preferred choice among steroids, especially for women. It avoids typical estrogenic issues like water retention and gynecomastia due to its non-aromatizing nature. Androgenic effects are present but relatively mild. Responsible use is key to minimizing potential adverse effects.
5. Administration of Oxandrolone
For Medical Use:
Dosages in medical scenarios typically range from 5-10mg per day, occasionally reaching 20mg based on patient response.
For Athletic Use:
Men often use 20-30mg per day for performance enhancement, with doses up to 80-100mg for more pronounced effects. Women generally find 5-10mg per day effective for their needs.
6. Oxandrolone Feedback: Efficacy and Athletic Performance
Oxandrolone’s efficacy in performance enhancement is notable. It aids in lean muscle preservation during cutting phases, contributes to increased strength without excessive weight gain, and is associated with enhanced muscular endurance. Its ability to stimulate red blood cell production also aids in endurance, making it a versatile steroid for various athletic needs.
Detailed Effects of Oxandrolone
The steroid’s anabolic nature significantly outweighs its androgenic potency, making it an excellent choice for athletes seeking strength and endurance gains without substantial mass increase. Its capacity to reduce Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) and counteract glucocorticoid hormones further amplifies its effectiveness. Additionally, Oxandrolone’s direct impact on fat loss through lipolysis sets it apart from many anabolic steroids.
Side Effects and Responsible Use
While Oxandrolone is among the more side effect-friendly steroids, it’s not entirely free from potential adverse reactions. These include mild androgenic effects like acne and hair loss in predisposed individuals and, in rare cases, virilization in women. Its hepatotoxic nature, albeit milder compared to other oral steroids, necessitates careful liver health management.
Administration Specifics and Considerations
The oral bioavailability of Oxandrolone allows for convenient dosing schedules. Men and women differ in their dosage requirements, with women responding well to much lower doses. Its use in cycles should be carefully planned, considering its impact on liver enzymes and the individual’s overall steroid regimen.
