Technical Information about Testosterone Propionate: An In-Depth Overview
Introduction
Testosterone Propionate stands as a significant milestone in the development of synthetic testosterone variants. It was one of the earliest forms of testosterone ever manufactured and set the stage for later advancements in steroid therapy. Unlike its predecessors, Testosterone Propionate was the first to feature an ester attached, revolutionizing the way testosterone could be used medically and in performance enhancement.
Product Profile
As a single ester testosterone compound, Testosterone Propionate has played a pivotal role in the field of androgen replacement therapy and performance enhancement. Developed by the pharmaceutical giant Schering in 1937, it marked a significant advance from the previously used testosterone suspensions that required frequent administrations. The propionate ester attached to the testosterone base controls the hormone’s release time, allowing for more stable blood levels with less frequent injections.
- Chemical Identifier: 4-androstene-3-one, 17beta-ol.
- Compound Structure: Testosterone base coupled with a Propionate ester.
- Manufactured by: Various companies.
- Recommended Usage:
- For Men:
- TRT (Testosterone Replacement Therapy): 25-50mg administered 2-3 times per week.
- Performance Enhancement: 100-200mg every other day.
- For Women: Generally not advised.
- For Men:
- Duration of Active Effects: Less than 2 days.
- Detection Period: Approximately 2-3 weeks.
- Anabolic and Androgenic Potency Balance: 100/100.
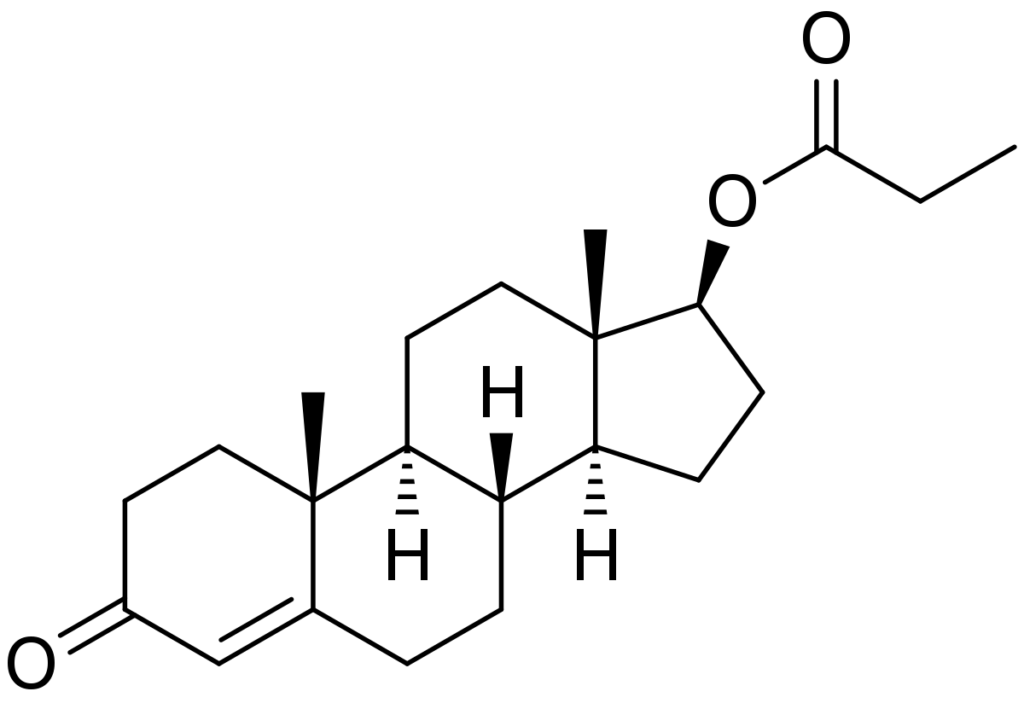
Testosterone Propionate Breakdown: Profiling Its Functional and Distinct Traits
Testosterone Propionate is characterized by the propionic acid ester attached to the testosterone molecule. This modification not only controls the release rate of testosterone into the bloodstream but also significantly affects its half-life, extending it to about two days post-administration. This esterification process was a major advancement, allowing for more manageable and efficient use of testosterone in various therapeutic and performance contexts.
Testosterone Propionate’s Diverse Impact: From Therapeutic to Performance Enhancement
Initially dominating the medical community until the 1960s, Testosterone Propionate was widely used for a variety of health issues, including low testosterone levels, certain menopausal issues, chronic cystic mastitis, excessive lactation, and endometriosis. In the world of performance enhancement, it gained popularity for its ability to produce less water retention, making it a preferred choice during cutting cycles. However, this belief is largely based on misconceptions about the ester’s impact on the hormone’s action.
Understanding Testosterone Propionate: Side Effects and Administration Guidelines
Despite its benefits, Testosterone Propionate is not without potential side effects. Estrogenic effects like gynecomastia, androgenic effects such as hair loss and acne, and cardiovascular impacts are all possible. These side effects can be mitigated with responsible use, including adherence to recommended dosages and the use of ancillary drugs when necessary.
Administration of Testosterone Propionate
For Medical Use
In therapeutic settings, Testosterone Propionate doses typically range from 25-50mg, administered 2-3 times weekly. This dosing schedule is designed to maintain stable testosterone levels, addressing symptoms associated with low testosterone such as reduced libido, muscle mass loss, and increased body fat.
For Sport Use
For athletes and bodybuilders, the dosing can vary widely. Ranges from 100mg every other day are common, providing significant enhancements in terms of muscle mass, strength, and recovery. The frequency of administration is key to maintaining stable blood levels of the hormone, which is crucial for achieving optimal performance enhancement effects.
Testosterone Propionate Feedback: Efficacy and Athletic Performance
Among performance athletes, Testosterone Propionate is revered for its efficacy and quick action. It is particularly favored during cutting phases for its reputed ability to reduce water retention. Moreover, its rapid action and shorter half-life allow for quicker adjustments in dosing, which is advantageous in managing side effects and tailoring the regimen to individual needs.
